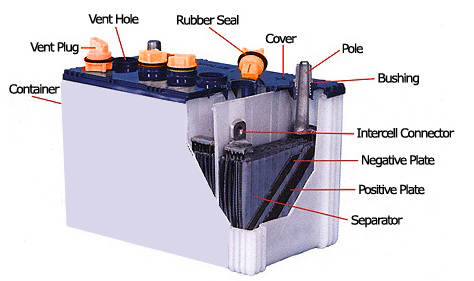
An automotive battery is a rechargeable battery that supplies electric energy to an automobile. The main purpose of the battery is to start the engine, lightings and stereos in the car as well ignition for the engine. Together with an alternator, it also acts a stabilizer to prevent voltage spikes.

A crucial component of the car engine that once the car is ignited, it transform the kinetic energy from the car movement and recharges the automotive battery.

Start stop technology delivers reduced carbon dioxide emissions by switching off the car’s engine when the vehicle comes to a stop. This technology delivers between 5% -10% lower emissions and enhanced fuel economy. Vehicles including Audi, BMW, Subaru, Volkswagen, Mercedes, Fiat, Mazda and even Proton now offer stop start vehicle options. In these vehicles, the battery is required to power headlights, stereos etc. while the vehicle is stationery as well as restarting the engine in an instant. Therefore different batteries are required to support these demands. These batteries are known as EFB or AGM Batteries. Fitting any other type of battery will significantly reduce its life and impair fuel savings.

Absorbed glass mat battery and differs from regular batteries in that the sulphuric acid (battery acid) is absorbed into the glass mats as opposed to the mats being submersed and “free floating” in the sulphuric acid. AGM battery enable the vehicles to cope with higher energy drains and demands that are needed to support new technology and accessory needs.

Enhance flooded battery is an entry level battery for vehicle that support start stop technology. EFB recovers more quickly than the standard batteries, as its application needs to be able to handle heavy duty, cyclic, start stop applications.

Sealed Maintenance-Free Batteries are not permanently sealed but are maintenance free. They can be oriented in any manner unlike normal lead–acid batteries. Sealed Maintenance Free batteries are designed for slow discharge. Car batteries are designed for rapid charge and rapid discharge.

The Battery Council International (BCI) is a trade association of manufacturers of original-equipment and after-market automobile batteries and other lead-acid batteries. It promotes the recycling of lead-acid batteries.

DIN is a standard for automobile electric terminal numbers, standardizing automobile with a number code. A different standard, EN 50005 recommends terminal numbering for general application relays (e.g. 11/12/14/A1/A2 for a SPDT relay) that may nevertheless be applied to automobiles. Since the introduction of modern fuel injected vehicles and the need for fast starting, the DIN standard has lost favor amongst automotive vehicle manufacturers.

Most older Japanese cars were fitted with JIS terminals. You must ensure that when you are buying a new battery that you know which terminals you have. One must also look at the orientation of and which side of the old battery the terminals are on.

Voltage refers to the amount of electrical potential your battery holds. The standard automotive battery in today’s vehicles is a 12-volt battery. Each battery has six cells, each with 2.1 volts at full charge. A car battery is considered fully charged at 12.6 volts or higher.
When the battery’s voltage drops, even a small amount, it makes a big difference in its performance. The table on the left shows how much energy remains in a battery as the battery voltage reading changes.
Though not fully charged, a car battery is considered charged at 12.4 volts or higher. It is considered discharged at 12.39 volts or less.
Note: A fully charged specific gravity of 1.265 corrected to 26.67°C is assumed.
Electrical energy in a battery is generated by a chemical reaction. In the case of a lead-acid battery, a mixture of sulfuric acid and water, known as electrolyte, reacts with active material inside the battery.
A battery’s voltage largely depends on the concentration of sulfuric acid. To get a voltage of 12.6 volts or higher, the weight percentage of sulfuric acid should be 35 percent or more. As a battery is discharged, the reaction between sulfuric acid and active material forms a different compound and the concentration of sulfuric acid declines. Over time, this causes the battery’s voltage to drop.

Vehicle engines require cranking power to start. The power needed depends on many factors, such as engine type, engine size and temperature. Typically, as temperatures drop, more power is needed to start the engine. Cold cranking amps (CCA) is a rating that measures a battery’s cranking power. It refers to the number of amps a 12-volt battery can deliver at -18°C for 30 seconds while maintaining a voltage of at least 7.2 volts. For example, a 12-volt battery with a 600 CCA rating means that at -18°C, the battery will provide 600 amps for 30 seconds without dropping below 7.2 volts.
